The Ultimate Manual for Therapists: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Therapy

Welcome to the ultimate manual for therapists, a comprehensive guide to the art and science of providing effective therapy. This manual is designed to equip therapists with the knowledge, skills, and resources necessary to help their clients achieve positive outcomes. We will delve into various aspects of therapy, including communication, assessment, treatment planning, and ethical considerations. By the end of this manual, you will have gained a deeper understanding of the therapeutic process and will be well-equipped to provide compassionate, effective, and evidence-based care to your clients.
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2394 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 230 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Effective Communication
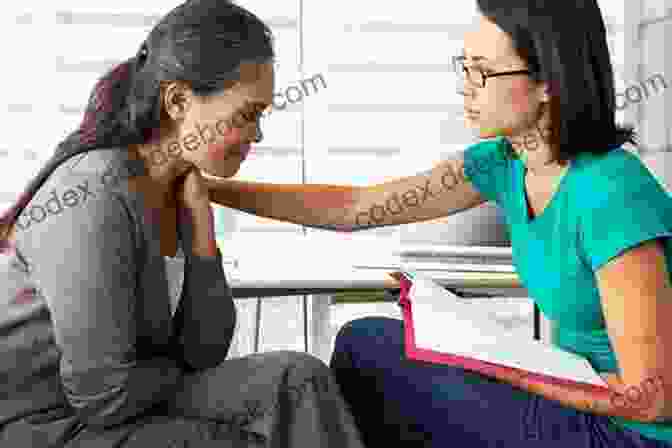

Effective communication is the foundation of successful therapy. Here are some key strategies to enhance your communication skills:
- Be an active listener. Show your client that you are fully engaged by maintaining eye contact, leaning in, and nodding in understanding. Ask clarifying questions to demonstrate that you are paying attention and to prevent misunderstandings.
- Use empathy. Try to understand your client's perspective, even if you don't agree with their beliefs or behaviors. Reflect their feelings back to them to show that you understand their emotional experience.
- Avoid judgment. Create a non-judgmental space where your client feels comfortable sharing their thoughts and feelings without fear of criticism or disapproval.
- Utilize verbal cues. Use verbal cues such as "I understand" or "It sounds like..." to acknowledge your client's statements and encourage them to continue sharing.
- Pay attention to non-verbal cues. Non-verbal cues can provide valuable insights into your client's feelings and thoughts. Observe their body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice to gain a better understanding of their communication.
Comprehensive Assessment

Thorough assessment is crucial to tailor therapy to each client's unique needs. Here are some key considerations for comprehensive assessment:
- Gather a thorough history. Collect information about your client's current concerns, past experiences, family background, and medical history. This information will help you understand the context of their presenting problems.
- Conduct a mental status exam. A mental status exam assesses a client's current cognitive, emotional, and behavioral functioning. This can help identify areas of impairment and rule out any underlying medical conditions.
- Use standardized assessments. Standardized assessments can provide objective measures of your client's symptoms and progress over time. These assessments can be used to track treatment outcomes and make informed treatment decisions.
- Collaborate with other professionals. If necessary, collaborate with other professionals such as physicians, psychiatrists, or social workers to obtain a comprehensive understanding of your client's situation.
- Continuously monitor progress. Regularly review your client's progress and adjust treatment plans as needed. This ensures that therapy remains relevant and effective as your client's needs evolve.
Treatment Planning and Intervention

Evidence-based treatment planning and intervention are essential for effective therapy. Here are some guidelines to consider:
- Set realistic goals. Collaborate with your client to establish realistic and achievable goals for therapy. These goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Tailor interventions to the client's needs. Choose therapeutic interventions that are appropriate for your client's specific concerns, goals, and learning style. Consider a variety of techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychodynamic therapy, or mindfulness-based interventions.
- Utilize evidence-based practices. Base your treatment decisions on the latest research and evidence-based practices. This ensures that your interventions are effective and supported by scientific evidence.
- Encourage active participation. Engage your client actively in the therapeutic process. Encourage them to participate in setting goals, identifying challenges, and developing coping strategies.
- Monitor and adjust the treatment plan. Regularly monitor your client's progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. This ensures that therapy remains relevant and effective.
Ethical Considerations and Boundaries

Adhering to ethical principles is paramount in therapy. Here are some key ethical considerations:
- Maintain confidentiality. Keep all client information strictly confidential unless they provide consent for disclosure or there is a legal requirement to report.
- Respect boundaries. Maintain appropriate professional boundaries with your clients, both physically and emotionally. Avoid any dual relationships that could compromise your objectivity.
- Obtain informed consent. Before starting therapy, ensure that your client fully understands the nature of therapy, their rights, and the potential risks and benefits involved.
- Practice cultural sensitivity. Be aware of and respect your client's cultural background, values, and beliefs. Avoid imposing your own values or biases on your client.
- Seek consultation and supervision. If you encounter ethical dilemmas or concerns, seek consultation from experienced colleagues or supervisors to ensure you are making sound ethical decisions.
This manual has provided a comprehensive overview of effective therapy practices, from communication and assessment to treatment planning and ethical considerations. Remember, every client is unique, and tailoring therapy to their individual needs is essential. By embracing the principles outlined in this guide, therapists can create a safe, supportive, and empowering therapeutic environment that fosters growth, resili
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2394 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 230 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Novel
Novel Text
Text Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback Newspaper
Newspaper Sentence
Sentence Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Narrative
Narrative Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Thesaurus
Thesaurus Character
Character Resolution
Resolution Card Catalog
Card Catalog Borrowing
Borrowing Stacks
Stacks Archives
Archives Periodicals
Periodicals Study
Study Research
Research Reserve
Reserve Rare Books
Rare Books Special Collections
Special Collections Interlibrary
Interlibrary Literacy
Literacy Study Group
Study Group Awards
Awards Reading List
Reading List Book Club
Book Club Lea Vandervelde
Lea Vandervelde Andrea Cremer
Andrea Cremer Petra Smit
Petra Smit Dave Ellis
Dave Ellis Irene Alexander
Irene Alexander Frank D Miele
Frank D Miele Lynn Michelsohn
Lynn Michelsohn Robin Robertson
Robin Robertson Lois J Zachary
Lois J Zachary David Mitchell
David Mitchell Maurice Possley
Maurice Possley Vic Parsons
Vic Parsons Mac Lethal
Mac Lethal Marcus E Ethridge
Marcus E Ethridge Anita Brearton
Anita Brearton Brian Reade
Brian Reade Debra Jacobs
Debra Jacobs August Strindberg
August Strindberg Robert P Saldin
Robert P Saldin Collette Scott
Collette Scott
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Dave SimmonsUnveiling the Enchantments of Tuscany: A Journey Through the Blue Guide to...
Dave SimmonsUnveiling the Enchantments of Tuscany: A Journey Through the Blue Guide to...
 Fred FosterHannah Montana Superstar Secrets Junior Novel 18: Uncovering the Secrets of a...
Fred FosterHannah Montana Superstar Secrets Junior Novel 18: Uncovering the Secrets of a... Albert CamusFollow ·4.7k
Albert CamusFollow ·4.7k Brayden ReedFollow ·12.3k
Brayden ReedFollow ·12.3k James GrayFollow ·12.6k
James GrayFollow ·12.6k Ian MitchellFollow ·14.8k
Ian MitchellFollow ·14.8k Beau CarterFollow ·18.7k
Beau CarterFollow ·18.7k Truman CapoteFollow ·5.2k
Truman CapoteFollow ·5.2k Devin CoxFollow ·13.9k
Devin CoxFollow ·13.9k Joshua ReedFollow ·17.1k
Joshua ReedFollow ·17.1k

 Tom Hayes
Tom HayesSunset Baby Oberon: A Riveting Exploration of Modern...
In the realm of...

 Barry Bryant
Barry BryantBefore Their Time: A Memoir of Loss and Hope for Parents...
Losing a child is a tragedy...

 Johnny Turner
Johnny TurnerRhythmic Concepts: How to Become the Modern Drummer
In the ever-evolving...

 Logan Cox
Logan CoxQualitology: Unlocking the Secrets of Qualitative...
Qualitative research is a...

 Daniel Knight
Daniel KnightUnveiling the Secrets of the Lake of Darkness Novel: A...
A Journey into Darkness...
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2394 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 230 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |